-
News Feed
- EXPLORE
-
Pages
-
Groups
-
Events
-
Blogs
-
Marketplace
-
Offers
-
Jobs
-
Developers
Parasitic Assembly - Force Functional Biomaterials

http://tezcan.ucsd.edu/index.php/research/
Design of Functional Biomaterials
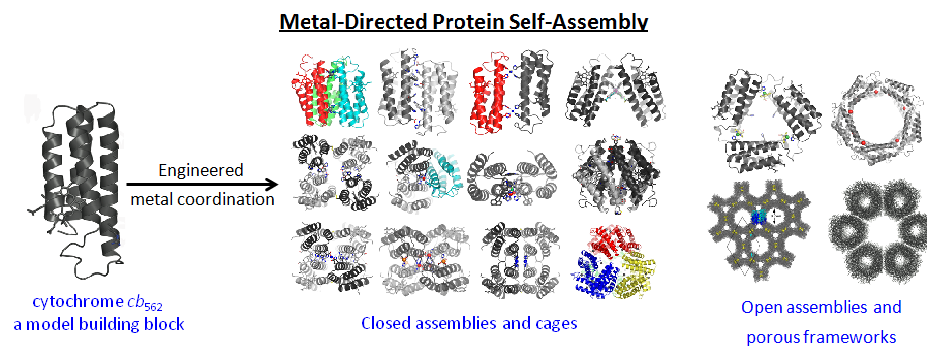
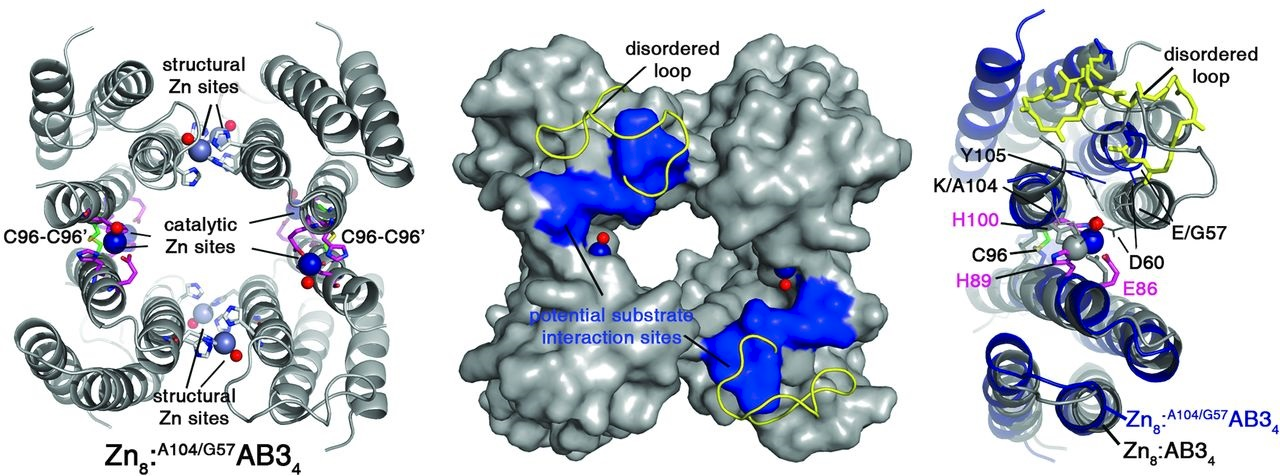
Evolution and Engineering of Inorganic Reactivity in Biological Scaffolds
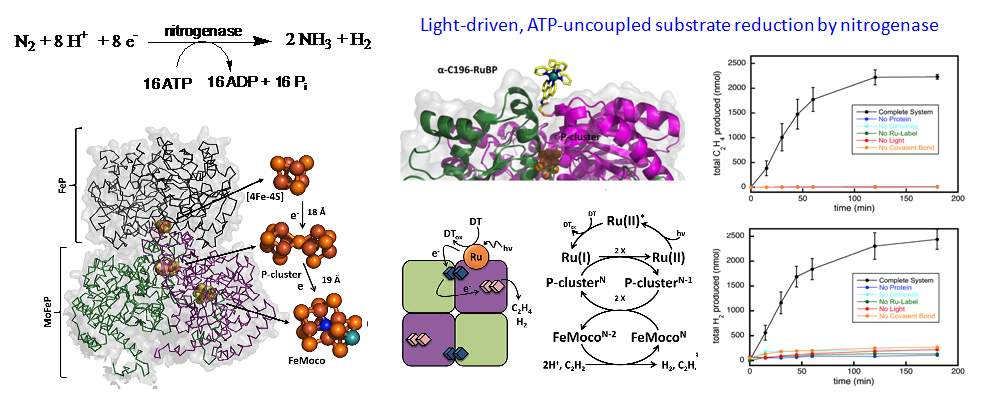
Elucidating the Molecular Mechanism of Biological Nitrogen Fixation
http://labs.feinberg.northwestern.edu/goldman/intro.htm
About Cytoskeletal Intermediate Filament Proteins
There are many Types of Intermediate Filaments
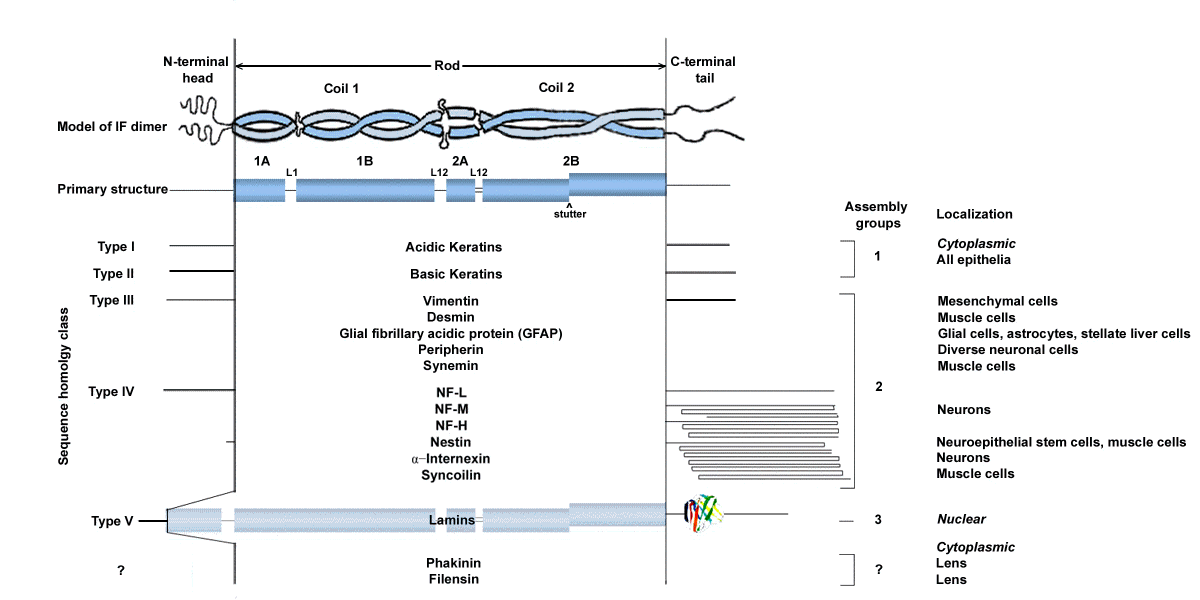

Intermediate filaments (IF) are the most diverse of the three major cytoskeletal systems in animal cells. The proteins comprising IF are encoded by approximately 70 different genes. This large family of proteins is subdivided into five types, four of which are located in the cytoplasm (cytoskeletal IF) and one in the nucleus (nucleoskeletal IF). In the cytoplasm, one, two or even more types of IF protein chains can polymerize into cytoskeletal IF of 10 nm diameter.
https://www.materialstoday.com/materials-chemistry/news/molecular-building-blocks-tessellations/ Materials Today Simple molecular building blocks self-assemble into complex tessel...
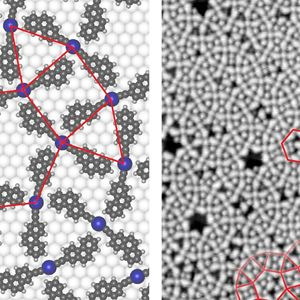
Simple molecular building blocks self-assemble into complex tessellations
Parquet floors, comprising a geometric mosaic of wood sections, are typically found in living rooms. But microstructured parquets, or rather tessellations, can occur in materials as well. Materials with such tessellations can possess some interesting properties, including outstanding electrical conductivity, special light reflection and extreme mechanical strength.
https://gab.ai/dicktripover/posts/24809060
https://www.reddit.com/r/titor/comments/8g0tny/parasitic_assembly_force_functional_biomaterials/

We are 100% funded for October.
Thanks to everyone who helped out. 🥰
Xephula monthly operating expenses for 2024 - Server: $143/month - Backup Software: $6/month - Object Storage: $6/month - SMTP Service: $10/month - Stripe Processing Fees: ~$10/month - Total: $175/month
- Art
- Causes
- Crafts
- Crime
- Dance
- Drinks
- Film
- Finance
- Fitness
- Food
- Games
- Gardening
- Health
- Home
- Literature
- Music
- Networking
- Paranormal
- Other
- Politics
- History
- News
- Party
- Science
- Religion
- Shopping
- Sports
- SyFy
- Politically Incorrect
- Philosophy
- Theater
- Technology
- Wellness



