#ClimateChange and
#GlobaklWarming is a
#HOAX!
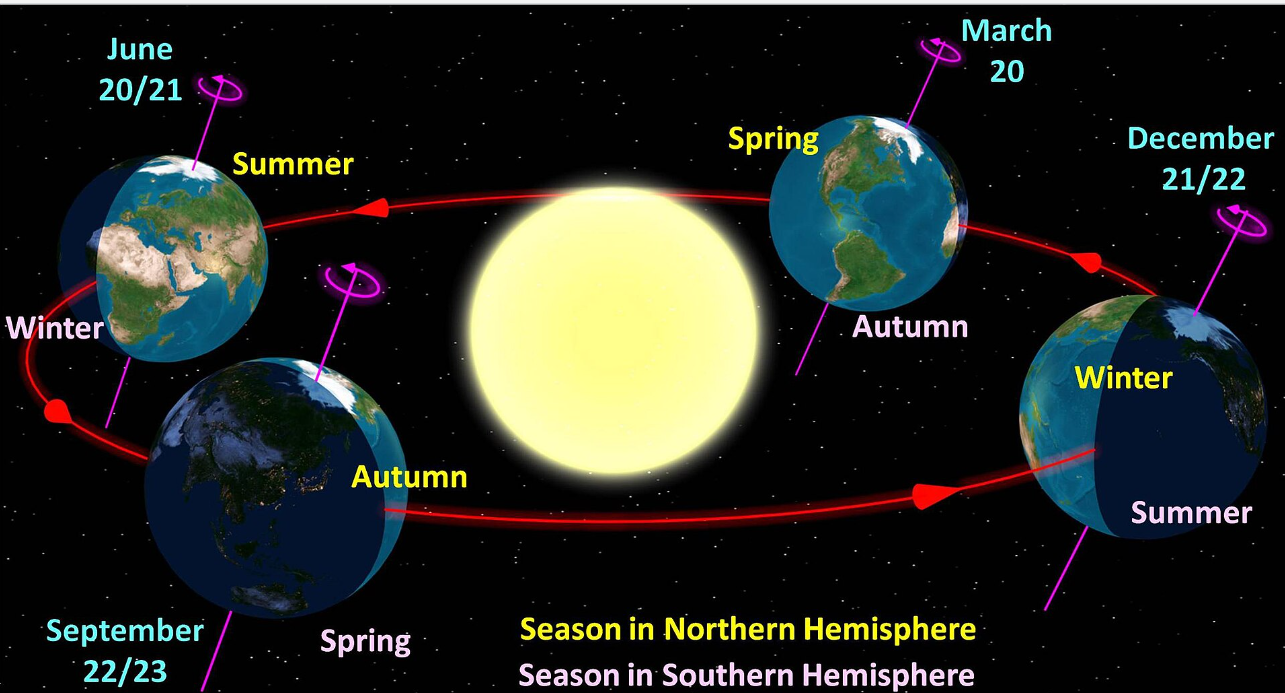
You have mentally ill people around the world claiming that CO2 is causing this BS "Climate Change" yet these same people generally have NO IDEA how much CO2 is even in our atmosphere! It's a mere 0.04% by the way, very little
CO2 is a gas of LIFE!
It is what humans exhale after breathing in oxygen...
And in PERFECT BALANCE the plants BREATHE IN CO2 AND EXHALE OXYGEN!
It's a perfect system. Yet, we have zealots bent on
#Eugenics who want to kill us all...
and if not KILL, they definitely want to CONTROL everyone! Their fictional
"Climate Change" narrative is designed to give them
FULL CONTROL OVER THE EARTH AND EVERYONE IN IT!
These
#Criminals will do whatever it takes to gain control over all of mankind!
And that includes spraying TOXINS into our skies, poisoning the entire agricultural system, all men and women, and even the water!
These lunatics have been trying to accomplish this
#Evil plan for over 150 years!
And it is time they are STOPPED!
These morons have no more rights to this earth than we do....
And there are BILLIONS OF US opposed to poisoning our earth and ourselves!
It's about time that we start acting like it!
These people belong in PRISON
Here's the short list of LIES we have been told about how
"Climate is going to kill us all" PURELY FICTION AND LIES!
Scientists seeking funding and journalists seeking an audience agree: panic sells.
“Global cooling is going to kills us all!” “No, wait: global warming is going to kill us all!”
Here's the list - an amazing chronology of the last 120 years of scare-mongering on climate
1895 - Geologists Think theWorld May Be Frozen Up Again – New York Times, February 1895
1902 - “Disappearing Glaciers…deteriorating slowly, with a persistency that means their final annihilation…scientific fact…surely disappearing.” – Los Angeles Times
1912 - Prof. Schmidt Warns Us of an Encroaching Ice Age – New York Times, October 1912
1923 - “Scientist says Arctic ice will wipe out Canada” – Professor Gregory of Yale University, American representative to the Pan-Pacific Science Congress, – Chicago Tribune
1923 - “The discoveries of changes in the sun’s heat and the southward advance of glaciers in recent years have given rise to conjectures of the possible advent of a new ice age” – Washington Post
1924 - MacMillan Reports Signs of New Ice Age – New York Times, Sept 18, 1924
1929 - “Most geologists think the world is growing warmer, and that it will continue to get warmer” – Los Angeles Times, in Is another ice age coming?
1932 - “If these things be true, it is evident, therefore that we must be just teetering on an ice age” – The Atlantic magazine, This Cold, Cold World
1933 - America in Longest Warm Spell Since 1776; Temperature Line Records a 25-Year Rise – New York Times, March 27th, 1933
1933 – “…wide-spread and persistent tendency toward warmer weather…Is our climate changing?” – Federal Weather Bureau “Monthly Weather Review.”
1938 - Global warming, caused by man heating the planet with carbon dioxide, “is likely to prove beneficial to mankind in several ways, besides the provision of heat and power.”– Quarterly Journal of the Royal Meteorological Society
1938 - “Experts puzzle over 20 year mercury rise…Chicago is in the front rank of thousands of cities thuout the world which have been affected by a mysterious trend toward warmer climate in the last two decades” – Chicago Tribune
1939 - “Gaffers who claim that winters were harder when they were boys are quite right… weather men have no doubt that the world at least for the time being is growing warmer” – Washington Post
1952 - “…we have learned that the world has been getting warmer in the last half century” – New York Times, August 10th, 1962
1954 - “…winters are getting milder, summers drier. Glaciers are receding, deserts growing” – U.S. News and World Report
1954 - Climate – the Heat May Be Off – Fortune Magazine
1959 - “Arctic Findings in Particular Support Theory of Rising Global Temperatures” – New York Times
1969 - “…the Arctic pack ice is thinning and that the ocean at the North Pole may become an open sea within a decade or two” – New York Times, February 20th, 1969
1969 – “If I were a gambler, I would take even money that England will not exist in the year 2000″ — Paul Ehrlich (while he now predicts doom from global warming, this quote only gets honorable mention, as he was talking about his crazy fear of overpopulation)
1970 - “…get a good grip on your long johns, cold weather haters – the worst may be yet to come…there’s no relief in sight” – Washington Post
1974 - Global cooling for the past forty years – Time Magazine
1974 - “Climatological Cassandras are becoming increasingly apprehensive, for the weather aberrations they are studying may be the harbinger of another ice age” –Washington Post
1974 - “As for the present cooling trend a number of leading climatologists have concluded that it is very bad news indeed” – Fortune magazine, who won a Science Writing Award from the American Institute of Physics for its analysis of the danger
1974 - “…the facts of the present climate change are such that the most optimistic experts would assign near certainty to major crop failure…mass deaths by starvation, and probably anarchy and violence” – New York Times
Cassandras are becoming increasingly apprehensive, for the weather aberrations they are studying may be the harbinger of another ice age
1975 - Scientists Ponder Why World’s Climate is Changing; A Major Cooling Widely Considered to Be Inevitable – New York Times, May 21st, 1975
1975 - “The threat of a new ice age must now stand alongside nuclear war as a likely source of wholesale death and misery for mankind” Nigel Calder, editor, New Scientist magazine, in an article in International Wildlife Magazine
1976 - “Even U.S. farms may be hit by cooling trend” – U.S. News and World Report
1981 - Global Warming – “of an almost unprecedented magnitude” – New York Times
1988 - I would like to draw three main conclusions. Number one, the earth is warmer in 1988 than at any time in the history of instrumental measurements. Number two, the global warming is now large enough that we can ascribe with a high degree of confidence a cause and effect relationship to the greenhouse effect. And number three, our computer climate simulations indicate that thegreenhouse effect is already large enough to begin to effect the probability of extreme events such as summer heat waves. – Jim Hansen, June 1988 testimony before Congress, see His later quote andHis superior’s objection for context
1989 -“On the one hand, as scientists we are ethically bound to the scientific method, in effect promising to tell the truth, the whole truth, and nothing but – which means that we must include all doubts, the caveats, the ifs, ands and buts. On the other hand, we are not just scientists but human beings as well. And like most people we’d like to see the world a better place, which in this context translates into our working to reduce the risk of potentially disastrous climate change. To do that we need to get some broad based support, to capture the public’s imagination. That, of course, means getting loads of media coverage. So we have to offer up scary scenarios, make simplified, dramatic statements, and make little mention of any doubts we might have. This “double ethical bind” we frequently find ourselves in cannot be solved by any formula. Each of us has to decide what the right balance is between being effective and being honest. I hope that means being both.” – Stephen Schneider, lead author of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change,Discover magazine, October 1989
1990 - “We’ve got to ride the global warming issue. Even if the theory of global warming is wrong, we will be doing the right thing – in terms of economic policy and environmental policy” – Senator Timothy Wirth
1993 - “Global climate change may alter temperature and rainfall patterns, many scientists fear, with uncertain consequences for agriculture.” – U.S. News and World Report
1998 - No matter if the science [of global warming] is all phony . . . climate change [provides] the greatest opportunity to bring about justice and equality in the world.” —Christine Stewart, Canadian Minister of the Environment, Calgary Herald, 1998
2001 - “Scientists no longer doubt that global warming is happening, and almost nobody questions the fact that humans are at least partly responsible.” – Time Magazine, Monday, Apr. 09, 2001
2003 - Emphasis on extreme scenarios may have been appropriate at one time, when the public and decision-makers were relatively unaware of the global warming issue, and energy sources such as “synfuels,” shale oil and tar sands were receiving strong consideration” – Jim Hansen, NASA Global Warming activist, Can we defuse The Global Warming Time Bomb?, 2003
2006 - “I believe it is appropriate to have an over-representation of factual presentations on how dangerous it is, as a predicate for opening up the audience to listen to what the solutions are, and how hopeful it is that we are going to solve this crisis.” — Al Gore, Grist magazine, May 2006
2006 – “It is not a debate over whether the earth has been warming over the past century. The earth is always warming or cooling, at least a few tenths of a degree…” —Richard S. Lindzen, the Alfred P. Sloan professor of meteorology at MIT
2006 – “What we have fundamentally forgotten is simple primary school science. Climate always changes. It is always…warming or cooling, it’s never stable. And if it were stable, it would actually be interesting scientifically because it would be the first time for four and a half billion years.” —Philip Stott, emeritus professor of bio-geography at the University of London
2006 - “Since 1895, the media has alternated between global cooling and warming scares during four separate and sometimes overlapping time periods. From 1895 until the 1930’s the media peddled a coming ice age. From the late 1920’s until the 1960’s they warned of global warming. From the 1950’s until the 1970’s they warned us again of a coming ice age. This makes modern global warming the fourth estate’s fourth attempt to promote opposing climate change fears during the last 100 years.” –Senator James Inhofe, Monday, September 25, 2006
2007- “I gave a talk recently (on fallacies of global warming) and three members of the Canadian government, the environmental cabinet, came up afterwards and said, ‘We agree with you, but it’s not worth our jobs to say anything.’ So what’s being created is a huge industry with billions of dollars of government money and people’s jobs dependent on it.” – Dr. Tim Ball, Coast-to-Coast, Feb 6, 2007
2008 – “Hansen was never muzzled even though he violated NASA’s official agency position on climate forecasting (i.e., we did not know enough to forecast climate change or mankind’s effect on it). Hansen thus embarrassed NASA by coming out with his claims of global warming in 1988 in his testimony before Congress” – Dr. John S. Theon, retired Chief of the Climate Processes Research Program at NASA, see above for Hansen quotes
You can find this article by searching : American Thinker August 4, 2014
"120 years of climate scares"
It's time to tell these liars and eugenicists that the jig is up!
And their little HOAX is over!
Just look at the lunacy these people are printing!
It’s Time to Engineer the Sky
Global warming is so rampant that some scientists say we should begin altering the stratosphere to block incoming sunlight, even if it jeopardizes rain and crops
https://www.scientificamerican.com/article/its-time-to-engineer-the-sky/
#ClimateChange and #GlobaklWarming is a #HOAX!
You have mentally ill people around the world claiming that CO2 is causing this BS "Climate Change" yet these same people generally have NO IDEA how much CO2 is even in our atmosphere! It's a mere 0.04% by the way, very little
CO2 is a gas of LIFE!
It is what humans exhale after breathing in oxygen...
And in PERFECT BALANCE the plants BREATHE IN CO2 AND EXHALE OXYGEN!
It's a perfect system. Yet, we have zealots bent on #Eugenics who want to kill us all...
and if not KILL, they definitely want to CONTROL everyone! Their fictional
"Climate Change" narrative is designed to give them
FULL CONTROL OVER THE EARTH AND EVERYONE IN IT!
These #Criminals will do whatever it takes to gain control over all of mankind!
And that includes spraying TOXINS into our skies, poisoning the entire agricultural system, all men and women, and even the water!
These lunatics have been trying to accomplish this #Evil plan for over 150 years!
And it is time they are STOPPED!
These morons have no more rights to this earth than we do....
And there are BILLIONS OF US opposed to poisoning our earth and ourselves!
It's about time that we start acting like it!
These people belong in PRISON
Here's the short list of LIES we have been told about how
"Climate is going to kill us all" PURELY FICTION AND LIES!
Scientists seeking funding and journalists seeking an audience agree: panic sells.
“Global cooling is going to kills us all!” “No, wait: global warming is going to kill us all!”
Here's the list - an amazing chronology of the last 120 years of scare-mongering on climate
1895 - Geologists Think theWorld May Be Frozen Up Again – New York Times, February 1895
1902 - “Disappearing Glaciers…deteriorating slowly, with a persistency that means their final annihilation…scientific fact…surely disappearing.” – Los Angeles Times
1912 - Prof. Schmidt Warns Us of an Encroaching Ice Age – New York Times, October 1912
1923 - “Scientist says Arctic ice will wipe out Canada” – Professor Gregory of Yale University, American representative to the Pan-Pacific Science Congress, – Chicago Tribune
1923 - “The discoveries of changes in the sun’s heat and the southward advance of glaciers in recent years have given rise to conjectures of the possible advent of a new ice age” – Washington Post
1924 - MacMillan Reports Signs of New Ice Age – New York Times, Sept 18, 1924
1929 - “Most geologists think the world is growing warmer, and that it will continue to get warmer” – Los Angeles Times, in Is another ice age coming?
1932 - “If these things be true, it is evident, therefore that we must be just teetering on an ice age” – The Atlantic magazine, This Cold, Cold World
1933 - America in Longest Warm Spell Since 1776; Temperature Line Records a 25-Year Rise – New York Times, March 27th, 1933
1933 – “…wide-spread and persistent tendency toward warmer weather…Is our climate changing?” – Federal Weather Bureau “Monthly Weather Review.”
1938 - Global warming, caused by man heating the planet with carbon dioxide, “is likely to prove beneficial to mankind in several ways, besides the provision of heat and power.”– Quarterly Journal of the Royal Meteorological Society
1938 - “Experts puzzle over 20 year mercury rise…Chicago is in the front rank of thousands of cities thuout the world which have been affected by a mysterious trend toward warmer climate in the last two decades” – Chicago Tribune
1939 - “Gaffers who claim that winters were harder when they were boys are quite right… weather men have no doubt that the world at least for the time being is growing warmer” – Washington Post
1952 - “…we have learned that the world has been getting warmer in the last half century” – New York Times, August 10th, 1962
1954 - “…winters are getting milder, summers drier. Glaciers are receding, deserts growing” – U.S. News and World Report
1954 - Climate – the Heat May Be Off – Fortune Magazine
1959 - “Arctic Findings in Particular Support Theory of Rising Global Temperatures” – New York Times
1969 - “…the Arctic pack ice is thinning and that the ocean at the North Pole may become an open sea within a decade or two” – New York Times, February 20th, 1969
1969 – “If I were a gambler, I would take even money that England will not exist in the year 2000″ — Paul Ehrlich (while he now predicts doom from global warming, this quote only gets honorable mention, as he was talking about his crazy fear of overpopulation)
1970 - “…get a good grip on your long johns, cold weather haters – the worst may be yet to come…there’s no relief in sight” – Washington Post
1974 - Global cooling for the past forty years – Time Magazine
1974 - “Climatological Cassandras are becoming increasingly apprehensive, for the weather aberrations they are studying may be the harbinger of another ice age” –Washington Post
1974 - “As for the present cooling trend a number of leading climatologists have concluded that it is very bad news indeed” – Fortune magazine, who won a Science Writing Award from the American Institute of Physics for its analysis of the danger
1974 - “…the facts of the present climate change are such that the most optimistic experts would assign near certainty to major crop failure…mass deaths by starvation, and probably anarchy and violence” – New York Times
Cassandras are becoming increasingly apprehensive, for the weather aberrations they are studying may be the harbinger of another ice age
1975 - Scientists Ponder Why World’s Climate is Changing; A Major Cooling Widely Considered to Be Inevitable – New York Times, May 21st, 1975
1975 - “The threat of a new ice age must now stand alongside nuclear war as a likely source of wholesale death and misery for mankind” Nigel Calder, editor, New Scientist magazine, in an article in International Wildlife Magazine
1976 - “Even U.S. farms may be hit by cooling trend” – U.S. News and World Report
1981 - Global Warming – “of an almost unprecedented magnitude” – New York Times
1988 - I would like to draw three main conclusions. Number one, the earth is warmer in 1988 than at any time in the history of instrumental measurements. Number two, the global warming is now large enough that we can ascribe with a high degree of confidence a cause and effect relationship to the greenhouse effect. And number three, our computer climate simulations indicate that thegreenhouse effect is already large enough to begin to effect the probability of extreme events such as summer heat waves. – Jim Hansen, June 1988 testimony before Congress, see His later quote andHis superior’s objection for context
1989 -“On the one hand, as scientists we are ethically bound to the scientific method, in effect promising to tell the truth, the whole truth, and nothing but – which means that we must include all doubts, the caveats, the ifs, ands and buts. On the other hand, we are not just scientists but human beings as well. And like most people we’d like to see the world a better place, which in this context translates into our working to reduce the risk of potentially disastrous climate change. To do that we need to get some broad based support, to capture the public’s imagination. That, of course, means getting loads of media coverage. So we have to offer up scary scenarios, make simplified, dramatic statements, and make little mention of any doubts we might have. This “double ethical bind” we frequently find ourselves in cannot be solved by any formula. Each of us has to decide what the right balance is between being effective and being honest. I hope that means being both.” – Stephen Schneider, lead author of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change,Discover magazine, October 1989
1990 - “We’ve got to ride the global warming issue. Even if the theory of global warming is wrong, we will be doing the right thing – in terms of economic policy and environmental policy” – Senator Timothy Wirth
1993 - “Global climate change may alter temperature and rainfall patterns, many scientists fear, with uncertain consequences for agriculture.” – U.S. News and World Report
1998 - No matter if the science [of global warming] is all phony . . . climate change [provides] the greatest opportunity to bring about justice and equality in the world.” —Christine Stewart, Canadian Minister of the Environment, Calgary Herald, 1998
2001 - “Scientists no longer doubt that global warming is happening, and almost nobody questions the fact that humans are at least partly responsible.” – Time Magazine, Monday, Apr. 09, 2001
2003 - Emphasis on extreme scenarios may have been appropriate at one time, when the public and decision-makers were relatively unaware of the global warming issue, and energy sources such as “synfuels,” shale oil and tar sands were receiving strong consideration” – Jim Hansen, NASA Global Warming activist, Can we defuse The Global Warming Time Bomb?, 2003
2006 - “I believe it is appropriate to have an over-representation of factual presentations on how dangerous it is, as a predicate for opening up the audience to listen to what the solutions are, and how hopeful it is that we are going to solve this crisis.” — Al Gore, Grist magazine, May 2006
2006 – “It is not a debate over whether the earth has been warming over the past century. The earth is always warming or cooling, at least a few tenths of a degree…” —Richard S. Lindzen, the Alfred P. Sloan professor of meteorology at MIT
2006 – “What we have fundamentally forgotten is simple primary school science. Climate always changes. It is always…warming or cooling, it’s never stable. And if it were stable, it would actually be interesting scientifically because it would be the first time for four and a half billion years.” —Philip Stott, emeritus professor of bio-geography at the University of London
2006 - “Since 1895, the media has alternated between global cooling and warming scares during four separate and sometimes overlapping time periods. From 1895 until the 1930’s the media peddled a coming ice age. From the late 1920’s until the 1960’s they warned of global warming. From the 1950’s until the 1970’s they warned us again of a coming ice age. This makes modern global warming the fourth estate’s fourth attempt to promote opposing climate change fears during the last 100 years.” –Senator James Inhofe, Monday, September 25, 2006
2007- “I gave a talk recently (on fallacies of global warming) and three members of the Canadian government, the environmental cabinet, came up afterwards and said, ‘We agree with you, but it’s not worth our jobs to say anything.’ So what’s being created is a huge industry with billions of dollars of government money and people’s jobs dependent on it.” – Dr. Tim Ball, Coast-to-Coast, Feb 6, 2007
2008 – “Hansen was never muzzled even though he violated NASA’s official agency position on climate forecasting (i.e., we did not know enough to forecast climate change or mankind’s effect on it). Hansen thus embarrassed NASA by coming out with his claims of global warming in 1988 in his testimony before Congress” – Dr. John S. Theon, retired Chief of the Climate Processes Research Program at NASA, see above for Hansen quotes
You can find this article by searching : American Thinker August 4, 2014
"120 years of climate scares"
It's time to tell these liars and eugenicists that the jig is up!
And their little HOAX is over!
Just look at the lunacy these people are printing!
It’s Time to Engineer the Sky
Global warming is so rampant that some scientists say we should begin altering the stratosphere to block incoming sunlight, even if it jeopardizes rain and crops
https://www.scientificamerican.com/article/its-time-to-engineer-the-sky/