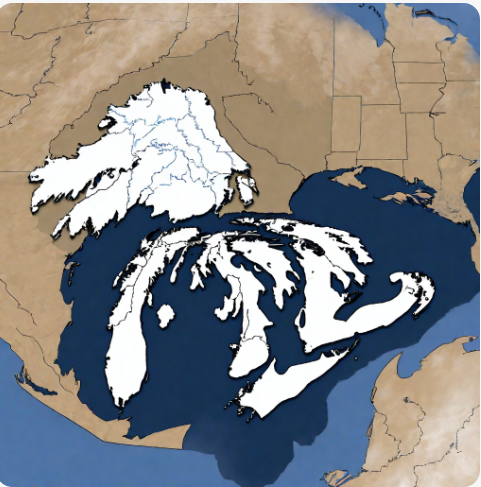
Lake-Effect Snow from Great Lakes Reaches Unprecedented Low in Mid-February
The Great Lakes region is known for its abundant snowfall during the winter months, with lake-effect snow contributing significantly to the overall snowpack. However, this year has been different, with coverage of the lakes reaching a historic low in mid-February snowfall during the winter months, with lake-effect snow contributing significantly to the overall snowpack. However, this year, the ice coverage on the lakes has reached an unprecedented low in mid-February, with the average temperature across the Great Lakes basin being 36°F (2°C) above normal in January.
The decreased ice coverage has potential consequences for the region's ecosystems and economy
The lack of ice cover can be attributed to warmer-than-usual temperatures in the region, which have prevented the formation of new ice and caused existing ice to melt earlier than usual. In fact, the average temperature across the Great Lakes basin was 36°F (2°C) above normal in January, making it the warmest January on record.
While some may welcome the absence of ice, it has significant implications for the environment and local communities. Ice plays an important role in regulating water levels, supporting fish populations, and providing habitat for wildlife. Additionally, the lack of ice cover can lead to increased evaporation, potentially affecting water supplies and shipping operations.
The decrease in ice coverage also impacts recreational activities such as ice fishing, snowmobiling, and skiing, which are popular pastimes in the region. Many businesses that rely on these activities have suffered losses due to the unseasonably warm weather.
However, not everyone is disappointed by the lack of ice. Shippers and cargo operators are benefiting from the open waters, as they can navigate the lakes more easily without having to worry about ice restrictions.
Despite the current conditions, it's important to note that ice coverage can fluctuate rapidly, and there's still a possibility of ice forming later in the season. The NOAA forecast suggests that ice coverage could rebound slightly in the coming weeks, but it's unlikely to reach historical averages.
In conclusion, while the unprecedented low ice coverage on the Great Lakes may bring some benefits to certain industries, it raises concerns about the long-term effects of climate change on the region's ecosystems and economy. As temperatures continue to rise, it's essential to monitor the situation closely and take steps to mitigate any negative consequences.
Lake-Effect Snow from Great Lakes Reaches Unprecedented Low in Mid-February
The Great Lakes region is known for its abundant snowfall during the winter months, with lake-effect snow contributing significantly to the overall snowpack. However, this year has been different, with coverage of the lakes reaching a historic low in mid-February snowfall during the winter months, with lake-effect snow contributing significantly to the overall snowpack. However, this year, the ice coverage on the lakes has reached an unprecedented low in mid-February, with the average temperature across the Great Lakes basin being 36°F (2°C) above normal in January.
The decreased ice coverage has potential consequences for the region's ecosystems and economy
The lack of ice cover can be attributed to warmer-than-usual temperatures in the region, which have prevented the formation of new ice and caused existing ice to melt earlier than usual. In fact, the average temperature across the Great Lakes basin was 36°F (2°C) above normal in January, making it the warmest January on record.
While some may welcome the absence of ice, it has significant implications for the environment and local communities. Ice plays an important role in regulating water levels, supporting fish populations, and providing habitat for wildlife. Additionally, the lack of ice cover can lead to increased evaporation, potentially affecting water supplies and shipping operations.
The decrease in ice coverage also impacts recreational activities such as ice fishing, snowmobiling, and skiing, which are popular pastimes in the region. Many businesses that rely on these activities have suffered losses due to the unseasonably warm weather.
However, not everyone is disappointed by the lack of ice. Shippers and cargo operators are benefiting from the open waters, as they can navigate the lakes more easily without having to worry about ice restrictions.
Despite the current conditions, it's important to note that ice coverage can fluctuate rapidly, and there's still a possibility of ice forming later in the season. The NOAA forecast suggests that ice coverage could rebound slightly in the coming weeks, but it's unlikely to reach historical averages.
In conclusion, while the unprecedented low ice coverage on the Great Lakes may bring some benefits to certain industries, it raises concerns about the long-term effects of climate change on the region's ecosystems and economy. As temperatures continue to rise, it's essential to monitor the situation closely and take steps to mitigate any negative consequences.