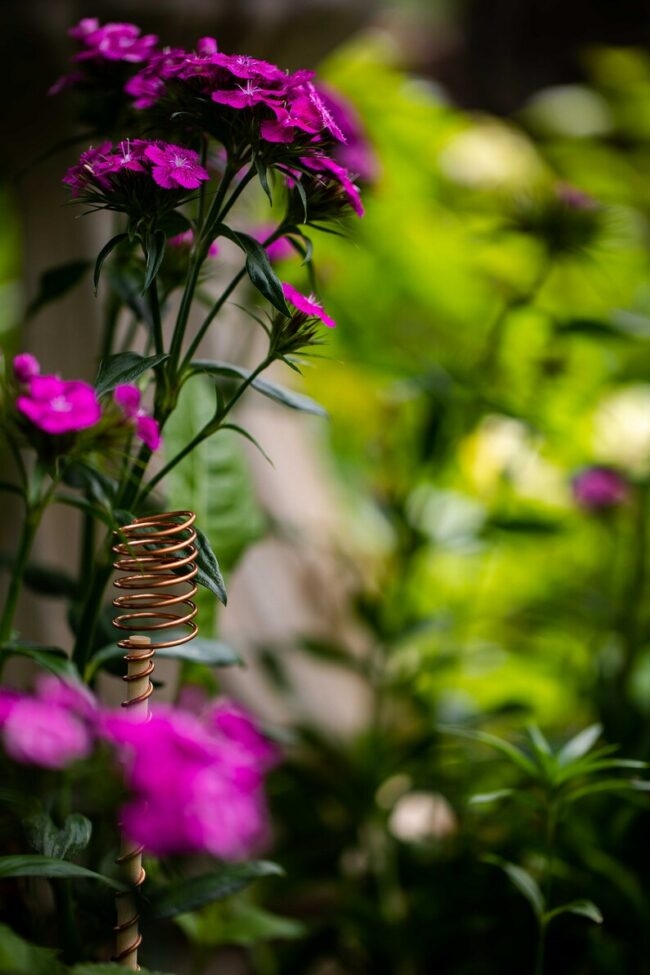
Electro-culture is a fascinating and innovative method that uses electrical stimulation to promote plant growth. The basic idea is that by exposing plants to electric fields or currents, you can influence their growth rates, health, and yields. Electro-culture antennas, specifically, are devices designed to capture and transmit ambient electromagnetic energy to plants.
Here’s how it works: the antennas are typically made from conductive materials and are placed around or above the plants. They can capture natural electromagnetic energy from the environment—like that from the Earth's natural electric field or from atmospheric electricity. This captured energy is then transmitted to the plants, theoretically enhancing their metabolic processes.
Studies and experiments have suggested various benefits, including improved seed germination rates, faster growth, greater biomass yield, and enhanced resistance to pests and diseases. The underlying mechanisms may involve stimulation of cellular activities and alteration of ion transport within the plants, leading to more efficient nutrient uptake and better overall plant vigor.
Electro-culture isn't mainstream yet, and much of the evidence supporting its effectiveness comes from small-scale experiments or anecdotal reports. However, for enthusiasts of sustainable agriculture or those looking for an edge in plant cultivation, exploring electro-culture could open up new possibilities. As with any innovative agricultural technology, it's advisable to combine it with established best practices for the best results.
Electro-culture is a fascinating and innovative method that uses electrical stimulation to promote plant growth. The basic idea is that by exposing plants to electric fields or currents, you can influence their growth rates, health, and yields. Electro-culture antennas, specifically, are devices designed to capture and transmit ambient electromagnetic energy to plants.
Here’s how it works: the antennas are typically made from conductive materials and are placed around or above the plants. They can capture natural electromagnetic energy from the environment—like that from the Earth's natural electric field or from atmospheric electricity. This captured energy is then transmitted to the plants, theoretically enhancing their metabolic processes.
Studies and experiments have suggested various benefits, including improved seed germination rates, faster growth, greater biomass yield, and enhanced resistance to pests and diseases. The underlying mechanisms may involve stimulation of cellular activities and alteration of ion transport within the plants, leading to more efficient nutrient uptake and better overall plant vigor.
Electro-culture isn't mainstream yet, and much of the evidence supporting its effectiveness comes from small-scale experiments or anecdotal reports. However, for enthusiasts of sustainable agriculture or those looking for an edge in plant cultivation, exploring electro-culture could open up new possibilities. As with any innovative agricultural technology, it's advisable to combine it with established best practices for the best results.