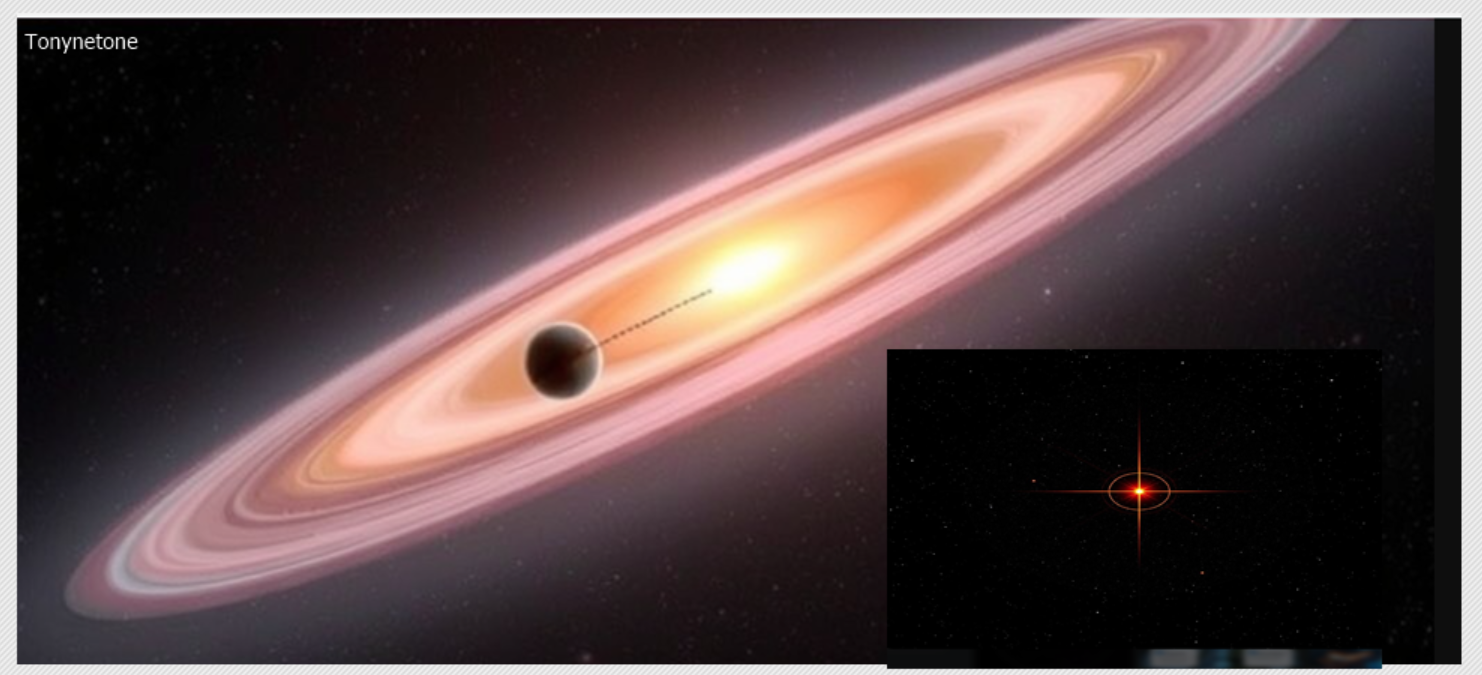
Barnard's Star the closest single star to the Sun, located about 6 light-years away in the constellation Ophiuchus. It is a red dwarf star, significantly smaller and dimmer than the Sun. While the Alpha Centauri system, which is about 4.37 light-years away, is closer, Barnard's Star holds the title for the closest solitary star.
In 2018, an international team of astronomers announced the discovery of a planet orbiting Barnard's Star, known as Barnard's Star b. This planet has a minimum mass around 3.2 times that of Earth, making it a super-Earth, and it orbits its star very closely—completing one orbit in about 233 Earth days. Its close proximity to the star places it in a cold region far from the habitable zone, as Barnard's Star is much cooler than the Sun.
As for the possibility of more planets, additional studies and observations are ongoing, and it's possible that future research could reveal more about the system.
In 2018, an international team of astronomers announced the discovery of a planet orbiting Barnard's Star, known as Barnard's Star b. This planet has a minimum mass around 3.2 times that of Earth, making it a super-Earth, and it orbits its star very closely—completing one orbit in about 233 Earth days. Its close proximity to the star places it in a cold region far from the habitable zone, as Barnard's Star is much cooler than the Sun.
As for the possibility of more planets, additional studies and observations are ongoing, and it's possible that future research could reveal more about the system.
Barnard's Star the closest single star to the Sun, located about 6 light-years away in the constellation Ophiuchus. It is a red dwarf star, significantly smaller and dimmer than the Sun. While the Alpha Centauri system, which is about 4.37 light-years away, is closer, Barnard's Star holds the title for the closest solitary star.
In 2018, an international team of astronomers announced the discovery of a planet orbiting Barnard's Star, known as Barnard's Star b. This planet has a minimum mass around 3.2 times that of Earth, making it a super-Earth, and it orbits its star very closely—completing one orbit in about 233 Earth days. Its close proximity to the star places it in a cold region far from the habitable zone, as Barnard's Star is much cooler than the Sun.
As for the possibility of more planets, additional studies and observations are ongoing, and it's possible that future research could reveal more about the system.
0 Comments
0 Shares
866 Views