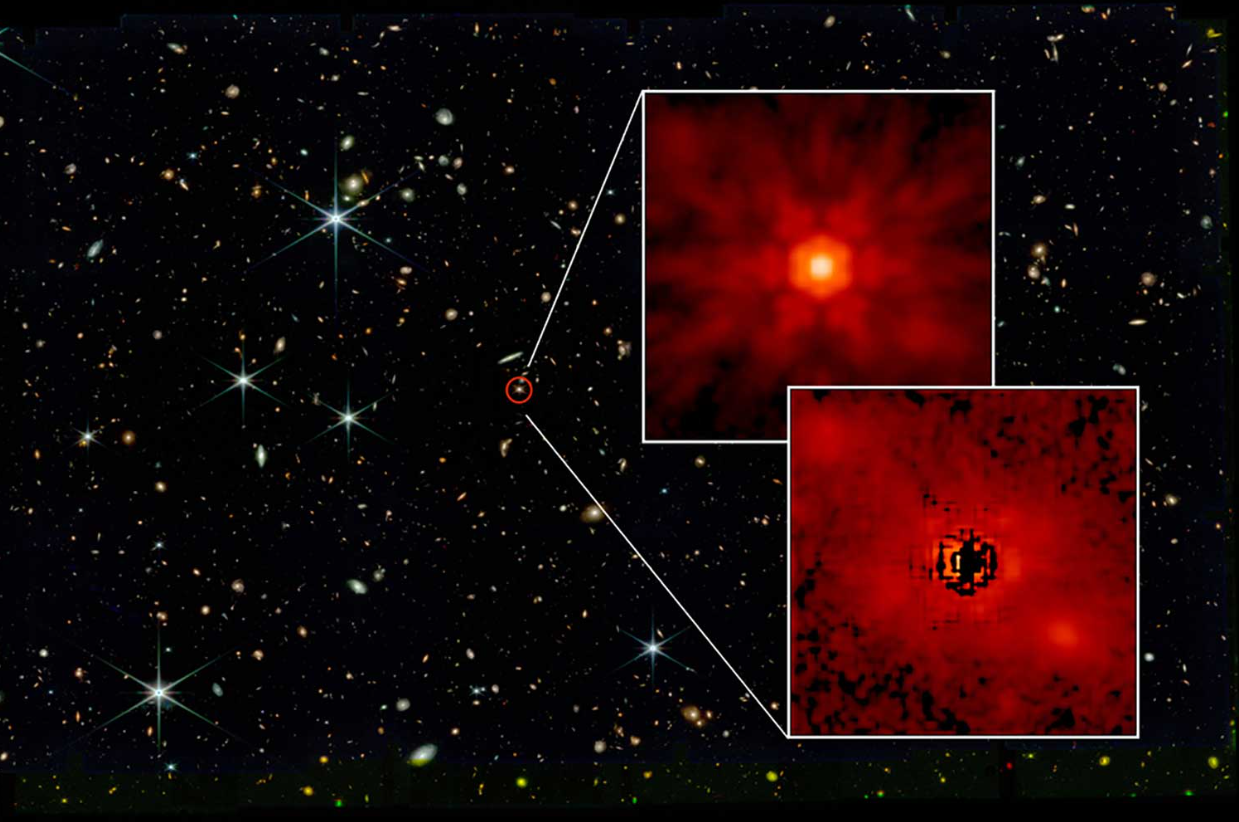
Another Jump in Astrophysics: Early Galaxies Challenging Dark Matter Models, The field of astrophysics has always been rife with surprising discoveries, and the latest findings from cutting-edge telescope data are no exception. Recent observations have cast doubt on some long-held assumptions about the formation of the early universe, leading scientists to question whether our current cosmological models, including the standard ΛCDM (Lambda Cold Dark Matter) model, truly represent the intricacies of cosmic evolution.
A Glimpse into Early Galaxies
Data from advanced telescopes, like the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST), has shown that early galaxies, formed less than a billion years after the Big Bang, were much larger and more luminous than previously believed possible. According to traditional models, galaxies were expected to grow more gradually, accruing mass and light over billions of years. The revelation that such massive and bright galaxies existed so early in the universe’s history has prompted a reevaluation of the ΛCDM model.
The Standard ΛCDM Model: A Quick Overview
The ΛCDM model is a mathematical framework that has long been the backbone of Big Bang cosmology. It consists of three main components:
A cosmological constant (Λ): This represents dark energy, an enigmatic force driving the accelerated expansion of the universe.
Cold dark matter (CDM): Hypothetical matter that does not emit or interact with electromagnetic radiation, explaining the unseen mass that affects gravitational forces on large scales.
Ordinary matter: The familiar atoms and particles that make up stars, planets, and everything else visible in the universe.
This model is referred to as the standard model of cosmology because it is the simplest and most comprehensive framework that has so far provided a reasonable explanation for a wide range of astronomical observations, from the cosmic microwave background to the distribution of galaxies.
Early Challenges and New Theories
However, the discovery of unexpectedly large and bright early galaxies implies that our models might be missing key details about the dynamics of the early universe. If galaxies formed so rapidly after the Big Bang, alternative explanations may be necessary. These might include modifications to our understanding of gravitational interactions on cosmic scales or the introduction of new interactions between particles that do not fit into the current ΛCDM framework.
Some astrophysicists are exploring models that propose dark matter behaves differently in the presence of extreme conditions, while others suggest entirely new mechanisms that accelerate the process of galaxy formation. These theories challenge the conventional narrative by suggesting that dark matter might not be a universal constant, or that additional factors, such as modified gravity theories, might come into play.
The Future of Cosmological Exploration
As these observations continue to be studied and debated, it is clear that our current cosmological models may need to be updated or expanded to align with this unexpected data. The insights gained from the JWST and similar telescopes will undoubtedly continue to push the boundaries of our understanding, leading to new theories that could redefine our comprehension of the universe’s origins and its early development.
The journey of discovery is far from over, and the universe, as always, holds more mysteries yet to be revealed. Whether these findings lead to small adjustments in the ΛCDM model or prompt the development of entirely new paradigms, one thing is certain: astrophysics is entering an exciting new chapter.
A Glimpse into Early Galaxies
Data from advanced telescopes, like the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST), has shown that early galaxies, formed less than a billion years after the Big Bang, were much larger and more luminous than previously believed possible. According to traditional models, galaxies were expected to grow more gradually, accruing mass and light over billions of years. The revelation that such massive and bright galaxies existed so early in the universe’s history has prompted a reevaluation of the ΛCDM model.
The Standard ΛCDM Model: A Quick Overview
The ΛCDM model is a mathematical framework that has long been the backbone of Big Bang cosmology. It consists of three main components:
A cosmological constant (Λ): This represents dark energy, an enigmatic force driving the accelerated expansion of the universe.
Cold dark matter (CDM): Hypothetical matter that does not emit or interact with electromagnetic radiation, explaining the unseen mass that affects gravitational forces on large scales.
Ordinary matter: The familiar atoms and particles that make up stars, planets, and everything else visible in the universe.
This model is referred to as the standard model of cosmology because it is the simplest and most comprehensive framework that has so far provided a reasonable explanation for a wide range of astronomical observations, from the cosmic microwave background to the distribution of galaxies.
Early Challenges and New Theories
However, the discovery of unexpectedly large and bright early galaxies implies that our models might be missing key details about the dynamics of the early universe. If galaxies formed so rapidly after the Big Bang, alternative explanations may be necessary. These might include modifications to our understanding of gravitational interactions on cosmic scales or the introduction of new interactions between particles that do not fit into the current ΛCDM framework.
Some astrophysicists are exploring models that propose dark matter behaves differently in the presence of extreme conditions, while others suggest entirely new mechanisms that accelerate the process of galaxy formation. These theories challenge the conventional narrative by suggesting that dark matter might not be a universal constant, or that additional factors, such as modified gravity theories, might come into play.
The Future of Cosmological Exploration
As these observations continue to be studied and debated, it is clear that our current cosmological models may need to be updated or expanded to align with this unexpected data. The insights gained from the JWST and similar telescopes will undoubtedly continue to push the boundaries of our understanding, leading to new theories that could redefine our comprehension of the universe’s origins and its early development.
The journey of discovery is far from over, and the universe, as always, holds more mysteries yet to be revealed. Whether these findings lead to small adjustments in the ΛCDM model or prompt the development of entirely new paradigms, one thing is certain: astrophysics is entering an exciting new chapter.
Another Jump in Astrophysics: Early Galaxies Challenging Dark Matter Models, The field of astrophysics has always been rife with surprising discoveries, and the latest findings from cutting-edge telescope data are no exception. Recent observations have cast doubt on some long-held assumptions about the formation of the early universe, leading scientists to question whether our current cosmological models, including the standard ΛCDM (Lambda Cold Dark Matter) model, truly represent the intricacies of cosmic evolution.
A Glimpse into Early Galaxies
Data from advanced telescopes, like the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST), has shown that early galaxies, formed less than a billion years after the Big Bang, were much larger and more luminous than previously believed possible. According to traditional models, galaxies were expected to grow more gradually, accruing mass and light over billions of years. The revelation that such massive and bright galaxies existed so early in the universe’s history has prompted a reevaluation of the ΛCDM model.
The Standard ΛCDM Model: A Quick Overview
The ΛCDM model is a mathematical framework that has long been the backbone of Big Bang cosmology. It consists of three main components:
A cosmological constant (Λ): This represents dark energy, an enigmatic force driving the accelerated expansion of the universe.
Cold dark matter (CDM): Hypothetical matter that does not emit or interact with electromagnetic radiation, explaining the unseen mass that affects gravitational forces on large scales.
Ordinary matter: The familiar atoms and particles that make up stars, planets, and everything else visible in the universe.
This model is referred to as the standard model of cosmology because it is the simplest and most comprehensive framework that has so far provided a reasonable explanation for a wide range of astronomical observations, from the cosmic microwave background to the distribution of galaxies.
Early Challenges and New Theories
However, the discovery of unexpectedly large and bright early galaxies implies that our models might be missing key details about the dynamics of the early universe. If galaxies formed so rapidly after the Big Bang, alternative explanations may be necessary. These might include modifications to our understanding of gravitational interactions on cosmic scales or the introduction of new interactions between particles that do not fit into the current ΛCDM framework.
Some astrophysicists are exploring models that propose dark matter behaves differently in the presence of extreme conditions, while others suggest entirely new mechanisms that accelerate the process of galaxy formation. These theories challenge the conventional narrative by suggesting that dark matter might not be a universal constant, or that additional factors, such as modified gravity theories, might come into play.
The Future of Cosmological Exploration
As these observations continue to be studied and debated, it is clear that our current cosmological models may need to be updated or expanded to align with this unexpected data. The insights gained from the JWST and similar telescopes will undoubtedly continue to push the boundaries of our understanding, leading to new theories that could redefine our comprehension of the universe’s origins and its early development.
The journey of discovery is far from over, and the universe, as always, holds more mysteries yet to be revealed. Whether these findings lead to small adjustments in the ΛCDM model or prompt the development of entirely new paradigms, one thing is certain: astrophysics is entering an exciting new chapter.
0 Commentaires
0 Parts
2KB Vue